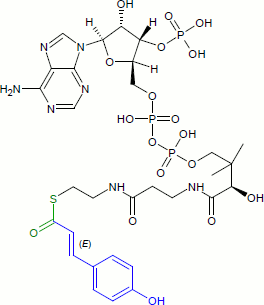
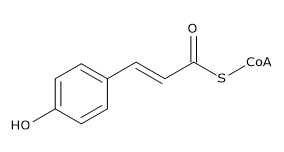
Coumaroyl-coenzyme A is the thioester of coenzyme-A and coumaric acid. Coumaroyl-coenzyme A is a central intermediate in the biosynthesis of myriad natural products found in plants. These products include lignols (precursors to lignin and lignocellulose), flavonoids, isoflavonoids, coumarins, aurones, stilbenes, catechin, and other phenylpropanoids.
Biosynthesis and significance
It is generated in nature from phenylalanine, which is converted by PAL to trans-cinnamate. Trans-cinnamate is hydroxylated by trans-cinnamate 4-monooxygenase to give 4-hydroxycinnamate (i.e, coumarate). Coumarate is condensed with coenzyme-A in the presence of 4-coumarate-CoA ligase:
- ATP 4-coumarate CoA AMP diphosphate 4-coumaroyl-CoA.
Enzymes using Coumaroyl-Coenzyme A
- Anthocyanin 3-O-glucoside 6''-O-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase
- Anthocyanin 5-aromatic acyltransferase
- Chalcone synthase
- 4-Coumarate-CoA ligase
- 6'-Deoxychalcone synthase
- Agmatine N4-coumaroyltransferase
- Flavonol-3-O-triglucoside O-coumaroyltransferase
- Naringenin-chalcone synthase
- Shikimate O-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase
- Trihydroxystilbene synthase
References